Shared Ingress
Motivation
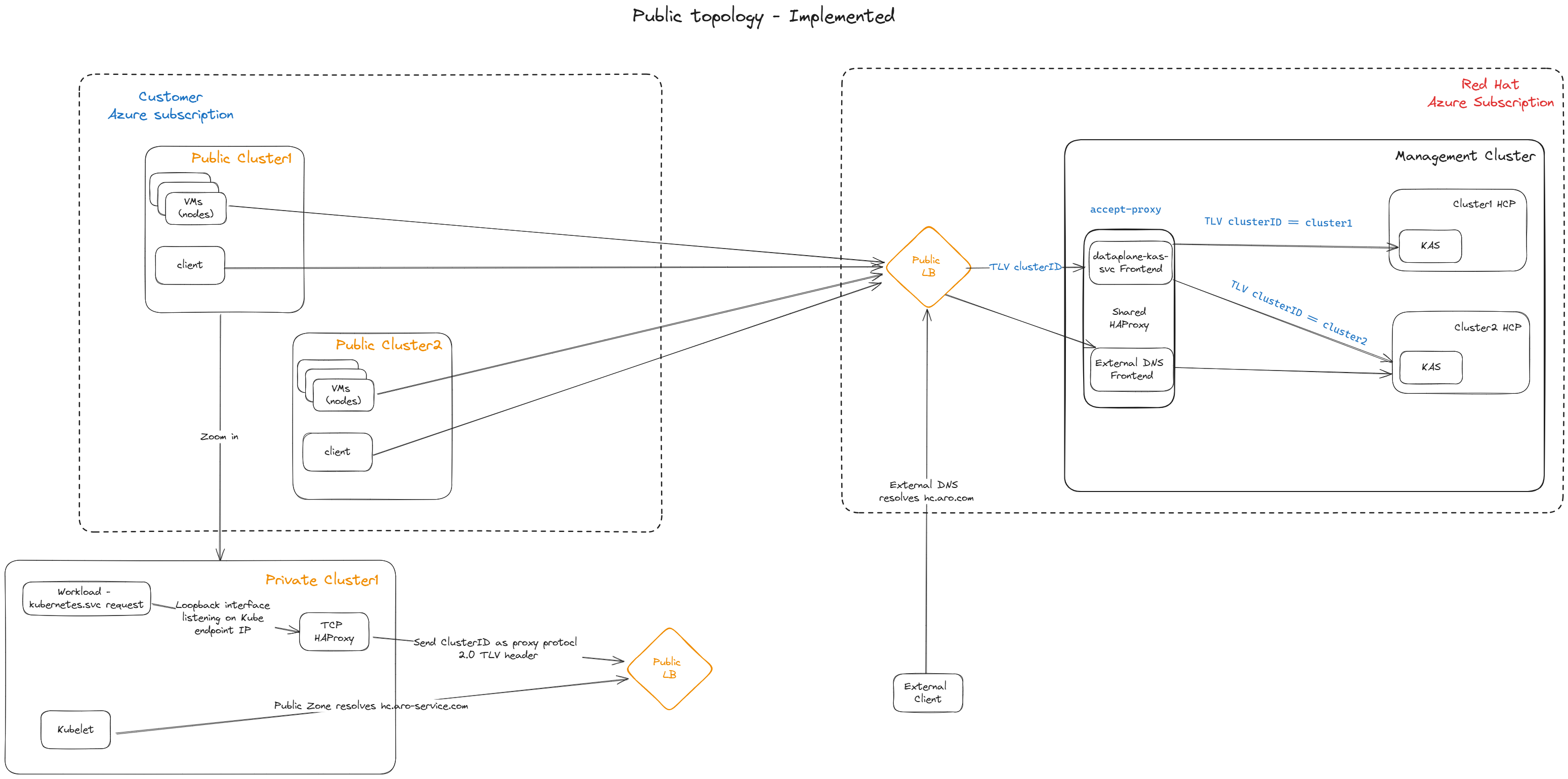
Today, exposing the apiserver of an hosted cluster to its nodes is possible only with two options: LoadBalancer and NodePort. The downside of the LoadBalancer method is that it would require a separate LB for every hosted cluster configured on the mgmt cluster. This can incur additional costs at the cloud provider and an additional, even if it small, spin up time to provision the LB service. The downside of the NodePort method is that it is bound to one of the nodes’ IP of the mgmt cluster (typically the 1st one). Once this node is down, all of the hosted clusters’ apiservers which are based on NodePort connectivity are no longer reachable. Shared Ingress presents another option, in which there would be a single LoadBalacer on the mgmt cluster, that will serve all of the hosted clusters that are configured to use this method. Connections to the hosted kube-apiservers from outside of the cluster will be made available through a Route.
Overview
Generally in kubernetes and openshift clusters, pods who wish to communicate with their cluster’s api-server, are doing it through the kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local master service, which is mapped to the cluster’s kube-apiserver service. In HyperShift guest clusters, the master service (whose IP is 172.31.0.1) is mapped to a kube-apiserver-proxy pod, running on every node at the host level, which proxies the request to the apiserver on the HCP namespace at the mgmt cluster, 1:1 flat translation, in TLS passthrough.
Shared Ingress (single LB) solution is able to differentiate between various hcp api-servers hosted on the mgmt cluster using the PROXY Protocol. The PROXY protocol enables adding additional info to a TLS connection, outside of the encrypted message, when both ends support this protocol. The fields that are added with the PROXY protocol are mainly: - Source IP - Source Port - Destination IP - Destination Port - TLVs (key-value pairs that carry arbitrary data)
Guest Intermediate Proxy
On the guest cluster, the kube-apiserver-proxy (HAProxy) instance, will use the PROXY protocol when sending requests and includes a custom TLV which contains the ClusterID so the central proxy on the mgmt can see ClusterID and forward it to the respective kube-apiserver on the hcp.
The default backend of this proxy will be the LB address of the central proxy.
MGMT Cluster Central Proxy
On the management cluster, we setup a single proxy server (HAProxy) in the hypershift-sharedingress namespace. This central proxy will accept connections through a LoadBalancer service, and with PROXY protocol.
It will then examine the custom TLV field of the PROXY protocol, extract the attached ClusterID and using an ACL, will forward the connection to the respective hcp kube-apiserver.
The destination IP in this case will be exactly the same as the ClusterIP of the hcp kube-apiserver.
Note: the kube-apiserver will no longer be exposed through a dedicated LB service.